Here is the C program to find transpose of a matrix. The transpose of a m x n matrix A, is another n x m matrix A^T by turning all the rows of a given matrix into columns and all the columns into rows.
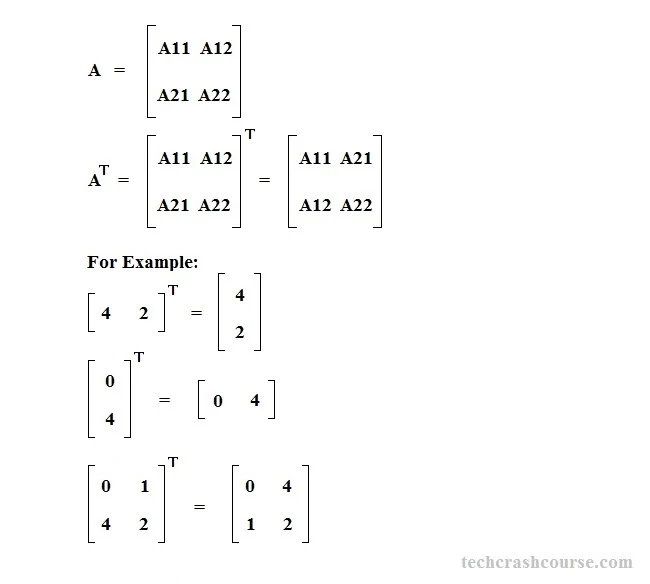
The transpose of matrix A is written A^T. The ithrow, jth column element of A is the jth row, ith column element of A^T. The transpose of a matrix A can be obtained by reflecting the elements along its main diagonal. If we repeat the process of transpose on a transposed matrix A^T, it returns A with elements in their original position.
Points to Remember
- The transpose of matrix A is written AT.
- The ith row, jth column element of A is the jth row, ith column element of AT.
- If A is an m × n matrix then AT is an n × m matrix.
Algorithm to find transpose of a matrix
Let A be the input matrix of size M x N and T be the transpose matrix of A(T = AT).
Let A be the input matrix of size M x N and T be the transpose matrix of A(T = AT).
- To find transpose of a matrix, we have to interchange the row and column index of every element. For example, an element of matrix A at position [i][j] will become an element of transpose matrix T at position[j][i](T[j][i] = A[i][j])
- Traverse matrix A row wise(first all elements of a row from left to right, then jump to next row) using two loops(check line number 23 and 24 of below program).
- For any element A[i][j], copy it's value to T[j][i](swap row and column indexes).
C program to find transpose of a matrix
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int rows, cols, rowCounter, colCounter;
int inputMatrix[50][50], transposeMatrix[50][50];
printf("Enter Rows and Columns of Matrix\n");
scanf("%d %d", &rows, &cols);
printf("Enter Matrix of size %dX%d\n", rows, cols);
for(rowCounter = 0; rowCounter < rows; rowCounter++){
for(colCounter = 0; colCounter < cols; colCounter++){
scanf("%d", &inputMatrix[rowCounter][colCounter]);
}
}
/* transpose[i][j] = inputMatrix[j][i] */
for(rowCounter = 0; rowCounter < rows; rowCounter++){
for(colCounter = 0; colCounter < cols; colCounter++){
transposeMatrix[colCounter][rowCounter] = inputMatrix[rowCounter][colCounter];
}
}
printf("Transpose Matrix\n");
/*Transpose Matrix of MXN = NXM Matrix */
for(rowCounter = 0; rowCounter < cols; rowCounter++){
for(colCounter = 0; colCounter < rows; colCounter++){
printf("%d ", transposeMatrix[rowCounter][colCounter]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter Rows and Columns of Matrix 2 3 Enter Matrix of size 2X3 1 2 3 4 5 6 Transpose Matrix 1 4 2 5 3 6
Enter Rows and Columns of Matrix 3 3 Enter Matrix of size 3X3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Transpose Matrix 0 3 6 1 4 7 2 5 8
Properties of Transpose Matrices
Let A be the input matrix of size M x N.
Let A be the input matrix of size M x N.
- The transpose of a transpose matrix is the original matrix
(AT)T = A - The transpose of two added matrices is the same as the addition of the two transpose matrices
(A + B)T = AT + BT - When a scalar element is multiplied to a matrix, the order of transposition is irrelevant
(sA)T = a(A)T - The transpose of a product of matrices equal the product of their transposes in reverse order
(AB)T = BTAT
Related Topics
